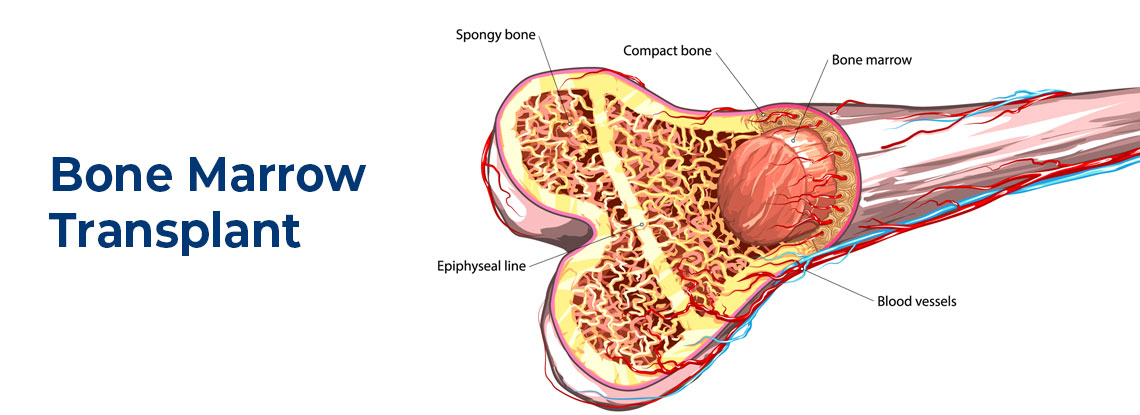
Introduction
Bone cancer develops in the skeletal system and destroys tissue. This means that it can move to other organs, like the lungs. Treatment options vary depending on the type of cancer they have. Some Bone Cancer Treatment are radiation therapy and chemotherapy. There is also a special type of treatment called surgery which removes the cancer cells or any affected parts of the bones inside and outside your body.
It’s more common in people over age 50. Bone cancers include osteosarcoma, soft tissue sarcoma (adult), chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma.
Types of Bone Cancer
Bone cancer, also called osteosarcoma, is a rare and aggressive form of cancer. It occurs most often in teens and young adults but can occur in children as well.
- Primary bone cancer occurs when cancer develops in the cells that produce or maintain the bones or cartilage.
- Secondary bone cancer occurs when cancers that develop elsewhere spread to the bones. With early detection.
Bone Cancer Treatment can cure many cases of primary bone cancer; however, this type of cancer sometimes spreads to other parts of the body before it is diagnosed.
Examples of primary bone tumors:
- osteochondroma.
- aneurysmal bone cyst.
- fibrous dysplasia of the bone.
- osteoma.
- osteoid osteoma.
- Enchondroma.
Osteoblastomas and giant cell tumors start in bone as benign growths. If a benign tumor becomes malignant, it is known as cancer. Osteoblastoma can become malignant. Giant cell tumors usually do not become cancerous. When either of these conditions spreads to distant sites or causes damage to nearby organs, it is rated as stage IV.
Bone Cancer Treatment Available
Bone Cancer Treatment Available Bone tumors result from abnormal cell growths in the bone. Treatment depends on the type of tumor and its location, how aggressive it is, and whether it has spread.
There are several approaches to treating bone cancer:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Cryosurgery
- Targeted therapy
- Chemotherapy
Grading and staging?
Grading and staging are ways to find out how advanced a cancer is. The grade describes the appearance of cells under a microscope, whether it is low grade or high grade, while staging reveals the extent or stage of disease in your body.
The staging and grading of a bone tumor allows doctors to determine how dangerous the tumor is and how best to treat it. The staging process establishes how far the cancer has spread by looking at whether or not it has entered nearby lymph nodes, while grading assesses the difference between healthy bone cells and malignant ones.
Risk factors of bone cancer?
Bone cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the bone marrow and spreads to other locations of the body. While best surgical oncologist in India still need to carry out more research into the precise cause of bone cancer, there are a range of risk factors associated with bone cancer. These include genetics, age and diet. They also indicate that people with long term inflammatory diseases, such as Paget’s disease, might be at a slightly higher risk of developing bone cancer later in life
Symptoms bone cancer
Pain is the most common symptom of bone cancer. It will feel like a dull ache or pain that cannot be explained. It will get worse over time and won’t subside with rest or treatment. If you’re experiencing this kind of pain, get help as soon as possible.
The progression of pain with Ewing sarcoma tends to be faster than in most other bone cancers. This is essentially due to the fact that this cancer usually affects small bones, for example around joints, meaning that there is not much bone in the area to protect it from movement.
- welling in the affected area.
- unintentional weight loss.
- a lump in the affected area.
- weak bones that lead to a significantly higher risk of fracture.
Other symptoms may include unintentional weight loss (if the cancer is in your stomach or intestines), fever, persistent night sweats, fatigue, depression and weakness in one part of your body.